Cancel
Start searching
This search is based on elasticsearch and can look through several thousand pages in miliseconds.
Learn moreWhether in a project or for your company's own infrastructure, the role of DevOps is becoming increasingly important!
The interaction of software and infrastructure is essential for the success of the project or your company.
Choosing the right infrastructure, tools and the appropriate configuration to ensure the security and quality standards for your software requires know-how and experience.
With our specialists, you benefit from our experience through consulting and implementation!

Our specialists will accompany you from start to finish and support you with their many years of experience and expertise. Even after successful implementation, our specialists will continue to be there for you to support you in ongoing operations, make adjustments, promote further development and offer training. Our specialists offer you the following:
With our DevOps specialists, you can use our extensive knowledge of the collaboration between software development and infrastructure for your project or company.
Our specialists have extensive experience in various software architectures and development processes. As a hosting provider, we also have a great deal of expertise in the area of infrastructure architecture.
You can decide whether we should only advise you or get directly involved in your project with our specialists. The advantage for you is that you do not have to set up or maintain your own DevOps resources in your company.
It is important to emphasize that the code developed for you (IaC) belongs to you. You are free to decide whether you want to work with us on a long-term basis or build up resources internally. We support you with documentation and training.
Depending on the nature of your project, we will be happy to advise you on the right infrastructure. We offer solutions for the entire spectrum, from smaller environments such as individual VMs to highly complex server infrastructures in your data center or in the cloud. if you already have an infrastructure, we will be happy to take over its operation and further development for you.
We attach great importance to high standardization of code quality (CI & CD) and security. In addition to automated tests and monitoring, we also keep an eye on your domain/infrastructure and adapt it to various threat scenarios.
If you have any questions about our services or the individual subject areas, please feel free to contact us. We have also explained the terms again for you in the "DevOps in a nutshell" section.
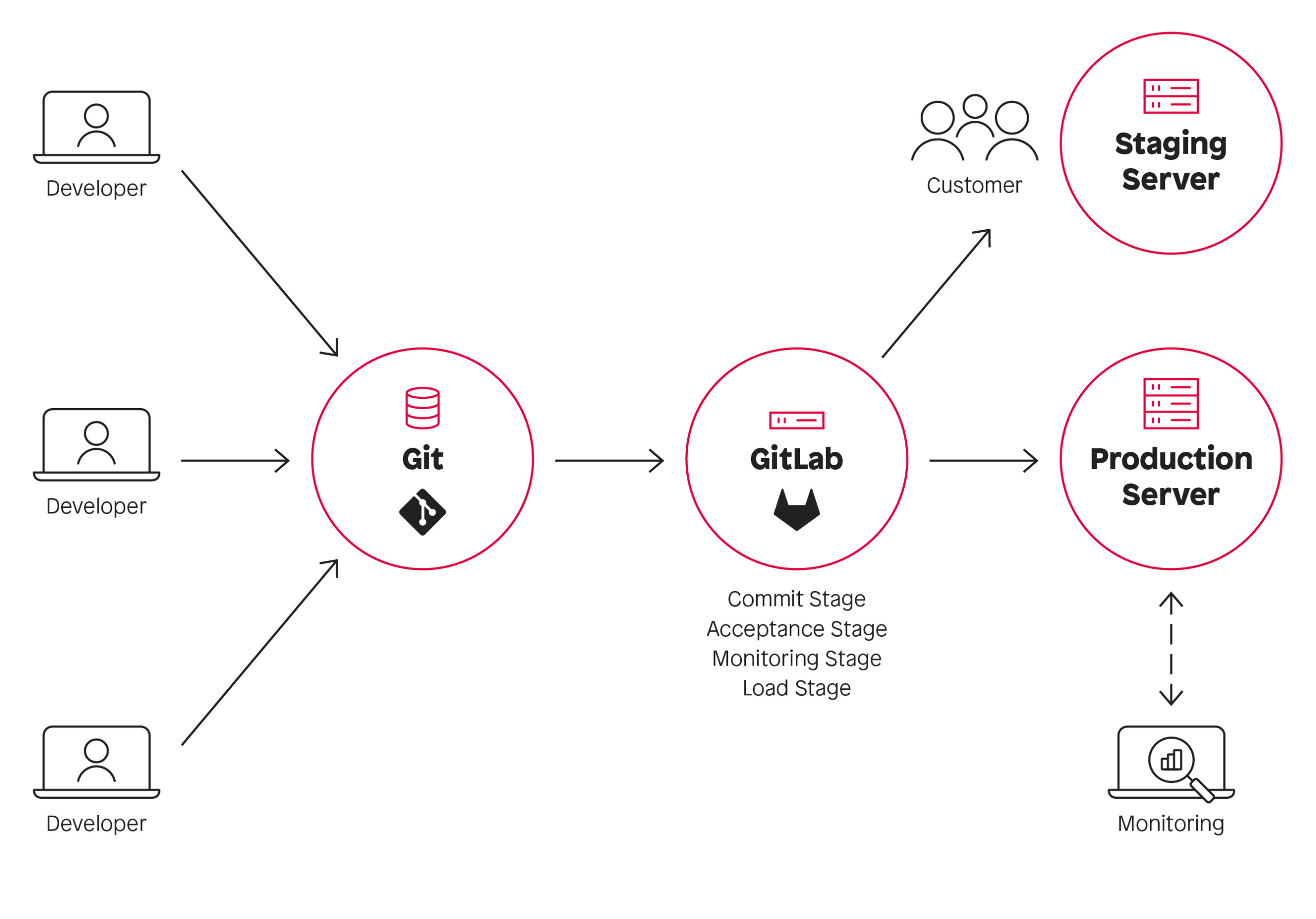
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are practices in the field of software development and DevOps that aim to optimize the development and deployment process.
Continuous Integration (CI):
Continuous Delivery (CD):
In summary, CI and CD promote automation, consistency and efficiency in the software development lifecycle, making development teams more agile and able to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably.
Microservices are an architectural method for the development of software applications in which an application is divided into smaller, independent services.
Each of these services, also known as microservices, fulfills a specific function and can be developed, implemented, scaled and updated independently of each other. This decentralized structure enables improved agility, flexibility and scalability in software development, as changes in one microservice have no impact on other parts of the application.
By using microservices, development teams can react more quickly to changes, facilitate maintenance and improve the overall reliability and scalability of the application.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a method in software development and DevOps in which the infrastructure required for the provision and execution of applications is described and managed using dedicated scripts or configurative definitions.
Instead of using manual processes or graphical user interfaces, the infrastructure is defined with code that is stored and managed in version control systems.
By using IaC, DevOps teams can automate the infrastructure, ensure repeatable and consistent deployments and respond more quickly to changes.
This enables more efficient management of resources, improved scalability and the ability to treat infrastructure like application code, reducing the gap between development and operations (Ops). IaC contributes to the agility, security and reliability of IT infrastructures.
Service monitoring refers to the preventive monitoring and analysis of IT services to ensure that they function efficiently and reliably. In the DevOps world, service monitoring plays a crucial role in ensuring the availability, performance and health of applications and services. Here are some key aspects:
Service monitoring helps to ensure the availability, reliability and performance of IT services, which is critical to ensuring a positive user experience and minimizing downtime.
Automated testing is a practice in the field of software development and in the DevOps approach, where specialized software tools are used to perform repeatable and predictable tests for software applications. The purpose of automated testing is to ensure the quality and stability of software during the development process.
In summary, automated tests include:
Automated testing helps to improve software quality, reduce development time and ensure application reliability by providing an efficient way to check software for errors and unwanted behavior.
Agile software development is an iterative and collaborative approach to software development that aims to respond flexibly to changes, better meet customer needs and achieve greater productivity in the development process. Here are the core principles of agile software development:
Agile software development promotes an adaptive and responsive approach that is particularly well suited to projects where requirements can change quickly. Agile methods such as Scrum or Kanban are often used in DevOps environments to enable efficient software development and delivery.